Galvanized steel pipe material
Release time: 15 Apr,2025
ID: 9
Views:
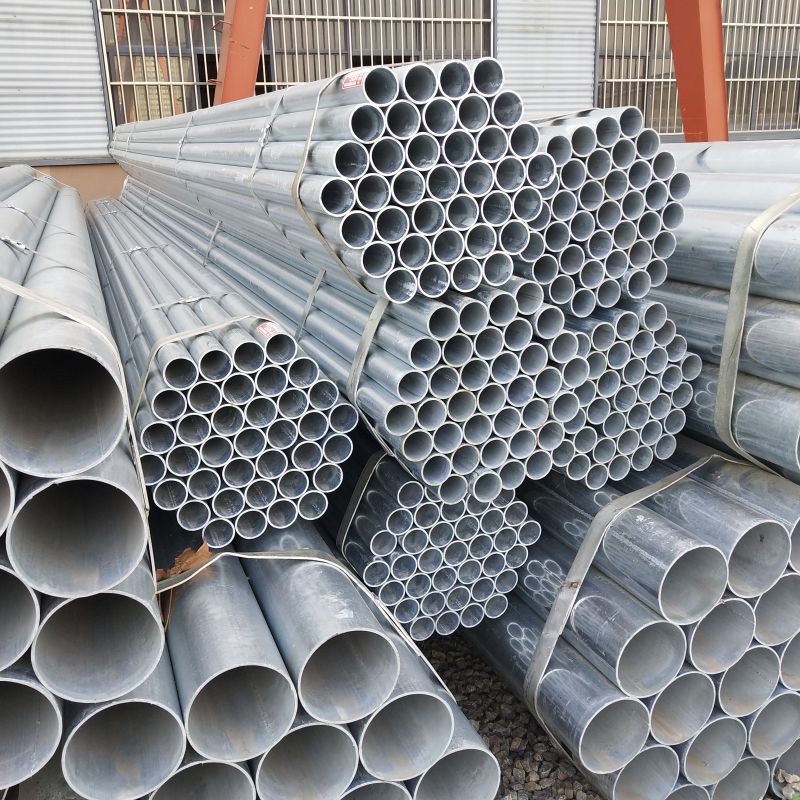

The material of galvanized pipe is usually carbon steel, and the base pipe (the steel pipe before galvanized) is mostly ordinary carbon structural steel or high-quality carbon steel, and the anticorrosive zinc layer is formed by hot dip galvanizing or electric galvanizing process. The following is the common classification and description of galvanized pipe materials:
The galvanized steel pipe substrate commonly used in the Chinese standard (GB/T 3091) has moderate strength, good plasticity and weldability, and is widely used in construction, water heating, low pressure fluid transportation and other fields.
- Q195
Low carbon content, good plasticity but slightly weak strength, often used in low-pressure pipelines, guardrail and other scenes with low strength requirements.
-20 # steel (high quality carbon structural steel)
Carbon content of about 0.2%, mechanical properties better than Q235, suitable for high pressure requirements, such as gas pipelines, mechanical structural parts, etc.
- SPCC (Japanese standard cold rolled carbon steel)
Used for electric galvanized steel pipe (such as wire bushing), the surface finish is high, but the corrosion resistance is weaker than hot dip galvanized.
- ST37, ST52 (European standard)
Corresponding to the German standard (DIN 2440/2441), ST37 is similar to Q235, ST52 is stronger and is used in industrial pipes.
The zinc layer is thick (usually 50-100μm), has strong anti-corrosion ability, and is suitable for outdoor or humid environments (such as fire pipes, scaffolding).
- Electrogalvanized (Electro-Galvanized)
The zinc layer is thin (5-20μm), the appearance is uniform but the corrosion resistance is poor, and it is mostly used for indoor wire bushing, furniture and so on.
- GB/T 3091: Galvanized welded steel pipe (Q235 substrate) for low pressure fluid transportation.
- GB/T 13793: straight welded galvanized steel pipe (Q195-Q345).
- American Standard (ASTM)
- ASTM A53: Galvanized seamless/welded steel pipe (Gr.B carbon steel).
- ASTM A123: Standard for structural parts of hot-dip galvanized steel.
- European Standard (EN)
- EN 10240: hot-dip galvanized steel pipe (base material S235, S355, etc.)
The outer layer is galvanized, the inner layer is stainless steel (such as 304), taking into account the anti-corrosion and health requirements, for high-end water supply systems.
- Galvanized aluminum-magnesium alloy tube
Aluminum and magnesium elements (such as Galvalume) are added to the zinc layer to further improve the weather resistance, suitable for coastal or chemical environments.
5. Matters needing attention
- Galvanized pipe can not be used to transport acid/strong alkaline media (zinc will react corrosion).
- Pay attention to the toxic gas produced by volatilization of zinc layer during welding, and ventilation is required for protection.
According to the specific use (pressure, environment, cost), you can choose different materials and galvanized steel pipes.
1. Base tube material
The galvanized steel pipe substrate commonly used in the Chinese standard (GB/T 3091) has moderate strength, good plasticity and weldability, and is widely used in construction, water heating, low pressure fluid transportation and other fields.
- Q195
Low carbon content, good plasticity but slightly weak strength, often used in low-pressure pipelines, guardrail and other scenes with low strength requirements.
-20 # steel (high quality carbon structural steel)
Carbon content of about 0.2%, mechanical properties better than Q235, suitable for high pressure requirements, such as gas pipelines, mechanical structural parts, etc.
- SPCC (Japanese standard cold rolled carbon steel)
Used for electric galvanized steel pipe (such as wire bushing), the surface finish is high, but the corrosion resistance is weaker than hot dip galvanized.
- ST37, ST52 (European standard)
Corresponding to the German standard (DIN 2440/2441), ST37 is similar to Q235, ST52 is stronger and is used in industrial pipes.
2. Influence of galvanizing process
The zinc layer is thick (usually 50-100μm), has strong anti-corrosion ability, and is suitable for outdoor or humid environments (such as fire pipes, scaffolding).
- Electrogalvanized (Electro-Galvanized)
The zinc layer is thin (5-20μm), the appearance is uniform but the corrosion resistance is poor, and it is mostly used for indoor wire bushing, furniture and so on.
3. International common standards
- GB/T 3091: Galvanized welded steel pipe (Q235 substrate) for low pressure fluid transportation.
- GB/T 13793: straight welded galvanized steel pipe (Q195-Q345).
- American Standard (ASTM)
- ASTM A53: Galvanized seamless/welded steel pipe (Gr.B carbon steel).
- ASTM A123: Standard for structural parts of hot-dip galvanized steel.
- European Standard (EN)
- EN 10240: hot-dip galvanized steel pipe (base material S235, S355, etc.)
4. Special purpose materials
The outer layer is galvanized, the inner layer is stainless steel (such as 304), taking into account the anti-corrosion and health requirements, for high-end water supply systems.
- Galvanized aluminum-magnesium alloy tube
Aluminum and magnesium elements (such as Galvalume) are added to the zinc layer to further improve the weather resistance, suitable for coastal or chemical environments.
5. Matters needing attention
- Galvanized pipe can not be used to transport acid/strong alkaline media (zinc will react corrosion).
- Pay attention to the toxic gas produced by volatilization of zinc layer during welding, and ventilation is required for protection.
According to the specific use (pressure, environment, cost), you can choose different materials and galvanized steel pipes.